Ac contactor working principle and internal structure diagram
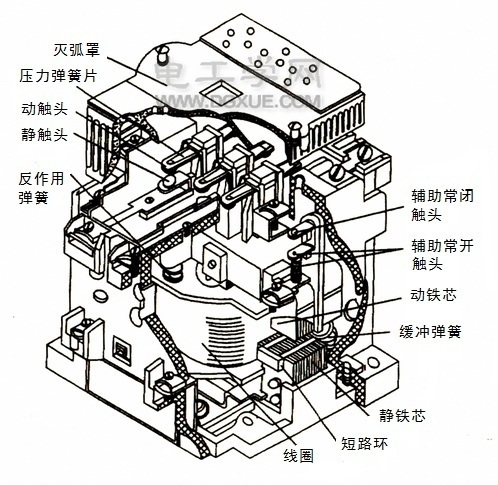
Electromagnetic system: It includes coil, static core and moving core (also known as armature).
Contact system: It includes main contact and auxiliary contact. The main contact allows a large current to pass through, which plays the role of connecting and cutting off the main circuit, usually the maximum current allowed through the main contact (that is, the rated current) as one of the technical parameters of the contactor. The auxiliary contact allows only a small current to pass through, and is generally connected to the control circuit when used.
The main contact of the AC contactor is generally a normally open contact, and the auxiliary contact has a normally open and a normally closed contact. Contactor with low rated current, with four auxiliary contacts; Higher rated current, with six auxiliary contacts. The three main contacts of the CJ10-20 contactor are normally open; It has four auxiliary contacts, two normally open and two normally closed.
The so-called normally open and normally closed refers to the state of the contact before the electromagnetic system is not powered on, that is, the normally open contact refers to the coil is not powered on, the dynamic and static contact is in a disconnected state, and the coil is closed after being powered on, so the normally open contact is also called the dynamic and static contact. After the coil is energized, it is disconnected, so the normally closed contact is also called the breaking contact.
The use of the arc extinguishing device is to quickly cut off the arc when the main contact is broken, which can be regarded as a large current, such as not quickly cut off, the main contact singting, welding and other phenomena will occur, so the AC contactor generally has an arc extinguishing device. For AC contactors with large capacity, arc suppression gate is often used.
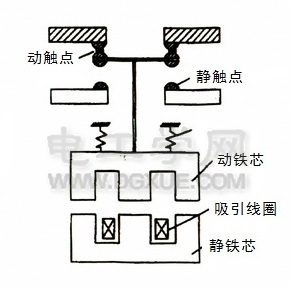
The working principle structure of the AC contactor is shown in the figure on the right. When the coil is energized, the iron core is magnetized and the armature is attracted to move downward, so that the normally closed contact is disconnected and the normally open contact is closed. When the coil is powered off, the magnetic force disappears, and under the action of the reaction spring, the armature returns to its original position, even if the contact is restored to its original state.

 Spain
Spain
 Portugal
Portugal

